Data and participants
This cross-sectional study analyzed data from the 2020 National Survey of Persons with Disabilities conducted by the Ministry of Health and Welfare and the Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. This is a nationally representative survey of community-dwelling persons with disabilities conducted every three years in Korea. Data from the National Survey of Persons with Disabilities are available on the Health and Welfare Data Portal (https://data.kihasa.re.kr/kihasa/kor/contents/ContentsList.html). In 2020, 7,025 registered persons with disabilities participated in the survey without considering household sampling due to the 2019 pandemic. [3].
The inclusion criteria for the current study were individuals with a physical disability and aged 20 years or older. Because propensity score matching should not include missing values, any individuals with missing values in the survey were excluded. A total of 1,757 eligible participants were extracted from the dataset of 7,025 samples (Appendix A).
countermeasure
Dependent Variable
The question about employment was, “Did you work for at least one hour in the last week to earn income?” and could be answered with two options: “Yes” or “No.” If the answer was “Yes,” the person was defined as employed.
Independent Variable
Based on previous studies, the independent variable was rehabilitation services. [8,9,10]Year [8, 9, 11, 12]sex [8,9,10,11, 13]spouse [8,9,10, 12, 14]Education [8, 10,11,12]monthly household income [11, 14]degree of disability [8, 9, 11, 13, 14]and subjective health status [11, 14]The question about rehabilitation services was “Are you currently receiving any rehabilitation?” and was recorded as a binary value, with a “yes” answer categorized as “has used rehabilitation services (=1)” and a “no” answer categorized as “has not used rehabilitation services (=0)”. The question about age, “What is your age?”, was recorded as a continuous variable. The question about gender was “What is your gender?”. This variable was also recorded as a binary value with two answers, “male (=1)” and “female (=0)”. The question about marital status, “Are you married?”, was recoded as a binary variable. It was categorized as “has a spouse (=1)” if the answer was “yes” and “no spouse (=0)” if the answer was “widowed, divorced, separated, or unmarried”. The question about education was “What is your highest educational attainment?” and was recorded as “kindergarten, preschool, primary school (=0)”. Subjective health status was assessed using a single question: ‘In general, how do you feel about your health?’ on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from ‘very bad (= 0)’ to ‘very good (= 5)’, with higher scores indicating better subjective health status.
Statistical analysis
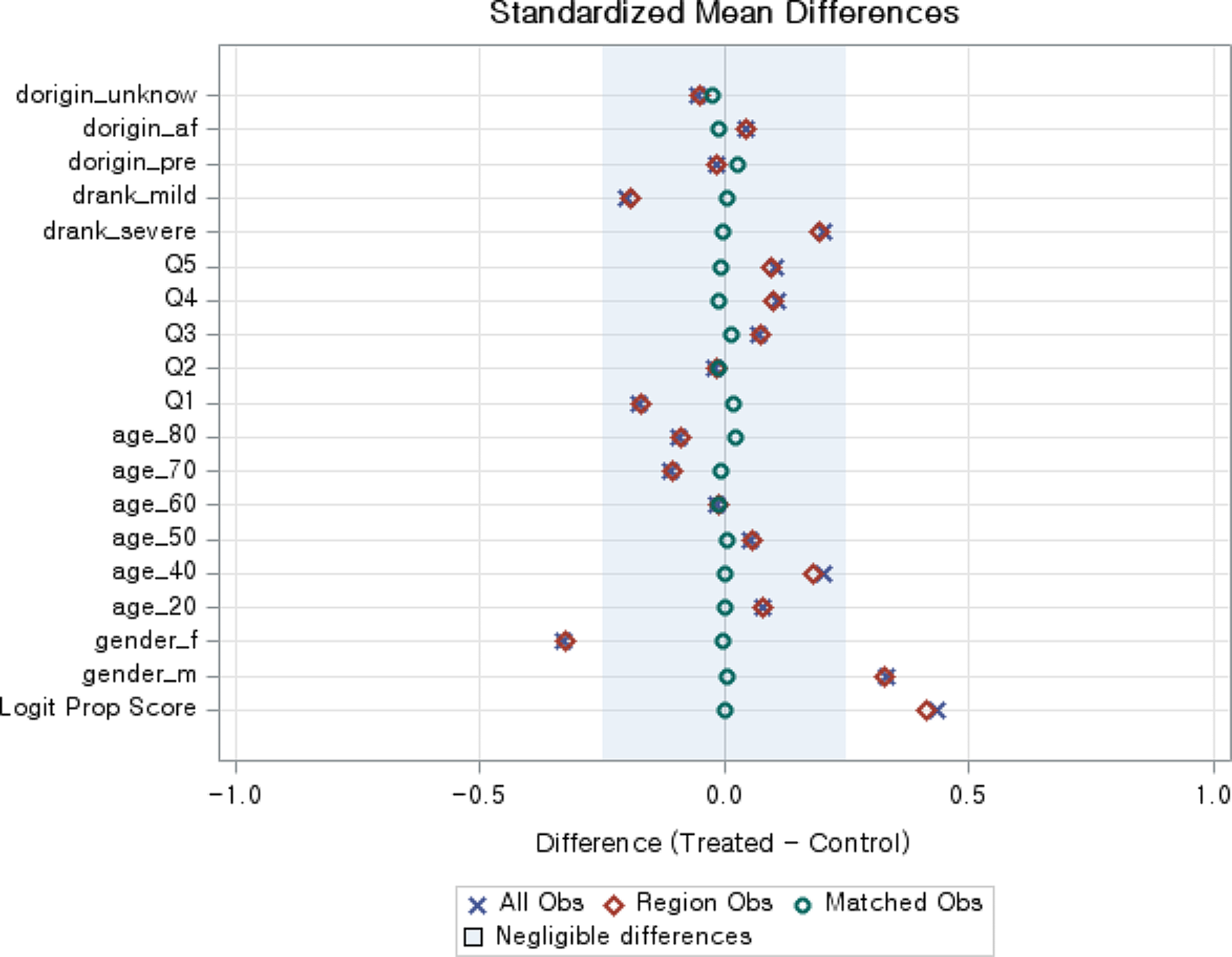
Data analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and SAS 9.4. First, propensity score matching was performed to reduce selection bias between the group that received rehabilitation services and the group that did not. In this study, a combination of nearest neighbor matching and caliper matching methods was applied. In this study, 1:1 ratio matching was applied, and the caliper range was 0.01. To verify the results of propensity score matching, paired t-tests were conducted and standardized mean differences were determined. [15]In the propensity score matching analysis, the dependent variable was the utilization of rehabilitation services. Based on previous studies, the independent variable was gender. [16, 17]Year [16, 18]monthly household income [16, 18]degree of disability [16]and the origins of the disorder [17]Appendix B provides more details on the description of the variables used for propensity score matching. Then, chi-square test and independent t-test were performed to see if there were differences in employment according to general characteristics in the propensity score matched data. Finally, logistic regression analysis was performed to estimate the effect of rehabilitation services on the employment of people with physical disabilities. Furthermore, factors that affect the employment of people with disabilities, such as gender (male, female), degree of disability (mild, severe), and subjective health status (good, poor), were divided into subgroups. Then, subgroup analysis was performed to determine whether the characteristics of each subgroup had an impact on employment. A sandwich estimator was applied for the logistic regression analysis.